Therapeutic Effect of Daphnetin on Mastitis Induced by Staphylococcus aureus in Mice
Yi LI, Qianjiong HUANG, Jinhui JIANG, Guoyang LIN, Chenchen HUANG, Jie GAO
1. Affiliated Hospital of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, China; 2. Department of Pathology and Pathophysiology, Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, China
Abstract [Objectives] To observe the effects of daphnetin on mastitis induced by Staphylococcus aureus in mice. [Methods] 18 postpartum ICR female mice were used to establish mastitis animal model, and were randomly divided into three groups (A, B, and C) with 6 mice in each group. Group A: blank control group; group B: S. Aureus model group; group C: S. Aureus model+daphnetin group. The experimental groups were injected 1 mL of 1.0×104 CFU/100 μL of S. aureus of along the nipple catheter. The suspension was placed in the 3rd and 4th pairs of mammary glands, and the control group was injected with the same dose of normal saline. On the second day after infection, the rats in group A, B and C were given drugs by gavage, while the rats in group A and B were given normal saline and the rats in group C were given daphnetin once a day for 6 consecutive days. Blood samples were collected from living eyeballs, and blood cells were analyzed by automatic flow cytometer after anticoagulation. [Results] The NLR and Systemie Immune Inflammati-on Index (SII) in the blood of mastitis mice induced by S. aureus were significantly higher than those in the control group (P<0.01), suggesting that neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and SII can be used as diagnostic indicators of mastitis, and the levels of NLR and SII decreased significantly after daphnetin intervention. [Conclusions] NLR and SII showed high levels in mastitis mice, which are valuable for the diagnosis of mastitis and the evaluation of its prognosis. After the intervention of daphnetin, both of them decreased significantly, indicating that daphnetin has a good prognosis trend in mastitis mice induced by S. aureus.
Key words Daphnetin, Mastitis, Staphylococcus aureus, Red cell distribution width (RDW), Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), Ratio of platelets to lymph-ocytes (PLR), Systemie Immune Inflammati-on Index (SII)
1 Introduction
Mastitis is an inflammatory disease of the mammary glands. It refers not only to the local breast tissue, but also to various inflammations related to breast tissue physiology, and is one of the common diseases in women during the puerperium. It has been previously reported that about 20% of women have a history of mastinitis infection. The mastitis is mainly caused by the invasion and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms, among which the main pathogenic bacteria areStaphylococcusaureus,EscherichiacoliandStreptococcus[1].S.aureuseasily leads to drug resistance to commonly used antibacterial drugs, and if not treated properly after infection, the disease will easily develop[2].S.aureuscan produce many pathogenic substances, such as various toxins and invasive enzymes, including enterotoxin, agglutination factor A, shock syndrome-1 toxin, α-hemolysin, β-hemolysin, leukocidin, fibronectin-binding protein, heat-resistant nuclease,etc[3-4]. If mastitis is not effectively controlled during lactation, various toxins produced by pathogenic bacteria will be rapidly absorbed by the body and spread throughout the body, leading to local breast tissue inflammation developing into systemic symptoms, which poses a major threat to human health[1]. Daphnetin (DPA) is an active component extracted from plants, also known as daphnetin, coumarin,etc., which belongs to benzopyrone compounds and has many pharmacological effects such as anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation[5]. The main mechanism of daphnetin’s pharmacological effect is to further promote the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines in the body by regulating NF-κB/TLR4 signaling pathway, so as to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduce inflammatory effects[6]. The red blood cell distribution width (RDW-CV) is one of the indicators reflecting the dispersion and distribution of peripheral red blood cellsinvivo, which is clinically used as a diagnostic and prognostic indicator for various types of anemia[7]. In recent years, various studies have found that RDW-CV is associated with the occurrence and development of various inflammatory diseases, and may be used to reflect the development and prognosis of various inflammatory diseases[8]. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and ratio of platelets to lymph (PLR) are widely considered to be stable in the immune state of inflammatory diseases[9]. NLR and PLR are often regarded as the evaluation indexes of inflammatory diseases, and have been applied to the diagnosis, detection and prognosis of inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis andUlcerativecolitis[10]. Systemic Immune Inflammation Index (SII) is a comprehensive inflammatory index obtained by measuring the product of neutrophil count and platelet count divided by lymphocyte count, which can well reflect the inflammation of the body[11]. RDW/NLR/PLR/SII are easily measurable indicators of inflammation. Up till now, however, there have been few reports on the use of daphnetin in the treatment of mastitis, so this study used the mouse mastitis model induced byS.aureus. We studied the effect of daphnetin on the mastitis induced byS.aureus. We analyzed RDW-CV, NLR, PLR and SII in the blood of mastitis mice induced byS.aureusto explore the preventive and therapeutic effects of daphnetin on mastitis and its potential mechanism.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
2.1.1Laboratory animal and strain. ICR mice aged 6 to 8 weeks were derived from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd.S.aureusstrain was obtained from the microbiological laboratory of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities. The breeders and their operations of all laboratory animals were approved by the Laboratory Animal Management and Use Committee of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, and conformed to theRegulationsontheManagementofLaboratoryAnimals.
2.1.2Main reagents. The daphnetin reagent CAS No.486-35-1 was purchased from Chengdu Pufei De Biotech Co., Ltd.; sodium citrate reagent was purchased from Anhui Zhongliao Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; HGH for injection was purchased from Hangzhou Guocang Instrument and Equipment Co., Ltd.
2.1.3Main instruments. The spectrophotometer was purchased from Shanghai Lichen Instrument Technology Co., Ltd.; the full automatic flow blood cell counter is from the Department of Medical Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities; 2 mL disposable vacuum negative pressure blood routine EDTA-K2 anticoagulant tube was purchased from Guangxi Guixiaohui Technology Co., Ltd.; Baird-Parker agar plate was purchased from Anhui Fencai Lingchuang Supply Chain Technology Co., Ltd.; 1 mL sterile syringe was purchased from Guangxi Guicaiyun Technology Co., Ltd.
2.2 Establishment of mouse mastitis model
2.2.1Culture and preparation of strains. InoculatedS.aureusin 7.5% NaCl broth medium, and then placed the inoculated medium in the incubator (37 ℃) for 6-8 h, and then streaked the culture on the Baird-Parker plate, and placed it in the incubator (37 ℃) for 18-24 h. Dipped a sterile cotton swab to take 3 to 5 single colonies and added them into 3 mL of sterile saline, mixed them well, took sterile saline as blank control, took 1 mL of bacterial suspension, and used a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 600 nm.ODvalue determination: if theODvalue is between 0.3 and 0.7, dilute the bacterial suspension with physiological saline gradient according to 0.5OD=1.0×108CFU/mL to obtain a suspension with a concentration of 1.0×104CFU/100 μL[12-14]for use.
2.2.2Grouping and treatment of experimental animals. 45 ICR mice (30 female and 15 male) aged from 6 to 8 weeks were fed for one week to adapt to the environment, and then the female mice were intraperitoneally injected with 0.1 mL of human gonadotropin per mouse, and the female and male mice were fed together at the ratio of 2:1. Adequate feed and water were given on time every day, and sperm suppositories were observed for 3 consecutive days. In the morning of the third day, 18 female rats were pregnant and randomly divided into three groups A, B and C, with 6 rats in each group. The weight of female rats was not comparable. A group: blank control group; B group:S.aureusmodel group; C group:S.aureusmodel+daphnetin group.
2.2.3Infection and medication. Female mice on the 5thto 7thday after delivery were used to establish mastitis animal model. Separated the young mice from the female mice 1 h in advance, anesthetized the female mice with 20% urartan, removed the lower abdominal fur of the female rats, exposed the nipples, and fixed the female mice on the operating table on their backs, and disinfected the 3rdand 4thpairs of nipples and the surrounding skin with iodophor. After lifting the third and fourth pairs of nipples with sterile forceps in hand, a small number (1 mm) of nipple tips were cut with sterilized ophthalmic scissors to expose the lactiferous ducts. Pipetted 1.0×104CFU/100 μL of suspension with a 1 mL sterile syringe and slowly inject 100 μL of the suspension along the lactiferous ducts into both pairs of mammary glands on average (Fig.1). The blank control group was injected with the same dose of normal saline. On the second day after the infection experiment, the three groups A, B and C were administered by gavage[15]. Six mice (A1-A6) in group A were treated with saline at a dose of 0.3 mL/mouse, six mice (B1-B6) in group B were treated with saline at a dose of 0.3 mL/mouse[16], and six mice (C1-C6) in group C were treated with daphnetin at a dose of 4 mg/kg[17], one time a day. After 6 d of continuous administration, about 1.5 mL of blood was taken from each animal by the method of blood sampling from living eyeballs[18], and separately placed in anticoagulant tubes. The blood was sent for examination within 2 h, and the experimental data of blood routine examination were provided by the Laboratory Department of the Affiliated Hospital of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities.

Fig.1 Mouse infection experiment
2.2.4Blood routine test. The female mice infected for 6 d were taken out and fixed with the left hand, and the blood was collected from the eyeball of the living body, and the blood was dropped into the EDTA-K2 anticoagulant tube, shaken properly to mix the blood with the anticoagulant evenly, and sent to the Laboratory Department of the Affiliated Hospital of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities within 2 h. The corresponding blood cells were analyzed by automatic flow cytometer, focusing on indicators such as RDW-CV, NLR, PLR and SII.
2.2.5Result judgment. RDW-CV, neutrophil count, lymphocyte count and platelet count were obtained. PLR, SII (platelet count×neutrophil count/lymphocyte count) and NLR can be obtained by calculation, and the results retained two decimal places, and the inflammatory indicators are reflected by RDW, NLR, PLR and SII indicators[17].
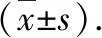
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Clinical manifestations and ocular pathological changes in miceThe female mice in group A did not show abnormal manifestations and symptoms, while the female mice in group B and C had relatively reduced feed intake and water intake, weakened activity, erect hair, coarse hair, malaise, slow response, curled up and arched back, and red and swollen breasts (Fig.2).

Fig.2 Infected mice
3.2 Levels of RDW-CV, NLR, PLR and SII in blood of mastitis mice and the effect of Rey pixel on themAccording to the experiment, the PLR of group B did not meet the normal distribution (Z=0.44,P<0.01), so the PLR was expressed by median (interquartile range)M(P25,P75). The results showed that there was no significant difference in RDW-CV and PLR among the three groups (P>0.05); compared with group A, the levels of NLR and SII in group B were significantly increased (P<0.01); compared with group B, the levels of NLR and SII in the blood of mice in group C were significantly decreased (P<0.01), as shown in Table 1.

Table 1 Effect of Rey pixel on the levels of RDW-CV, NLR, PLR and SII in blood of mastitis mice or M (P25, P75)
4 Discussion
Mastitis is a common disease in postpartum lactating women, and once getting the disease, it is easy to recur, and even further develop into lactating breast abscess, which requires abscess incision and drainage treatment, thereby delaying recovery and seriously damaging the health of the mother and baby[19]. The mastitis often refers to the local inflammatory infiltration of breast tissue. The main clinical manifestations are the four symptoms of redness, swelling, heat and pain, as well as the hypofunction of some breast tissues in the inflamed and infected areas. At present, antibiotics are commonly used in the clinical treatment of mastitis, but it is easy to produce adverse effects such as antibiotic residues and strain variation, which cause serious harm to the social medical and health undertakings[20]. Therefore, it is of great significance to find another means of treating mastitis without antibiotics.
The daphnetin is one of the coumarin-derived extracts, and many studies have shown that the daphnetin has anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, anticoagulant, antioxidant and other effects[21-22]. At present, daphnetin is mainly used to treat coronary heart disease and thrombotic occlusion. Daphnetin also has a role in the treatment of numerous inflammation-related diseases. Studies have shown that daphnetin can inhibit proinflammatory factors and block signaling pathways related to inflammation[23]. RDW-CV, NLR, PLR and SII are inflammatory indicators that are easy to measure and record in scientific research experiments, which can better feed back the inflammatory infection status of the body, and the levels of the four inflammatory indicators are related to the diagnosis and prognosis of various types of inflammation[24].
In this study, daphnetin intervention in the treatment of RDW-CV, NLR, PLR and SII were analyzed in the blood of mastitis mice induced byS.aureus. The levels of NLR and SII in the blood of mastitis mice induced byS.aureuswere significantly higher than those in the control group, and the levels of NLR and SII in the blood of mastitis mice induced byS.aureuswere significantly decreased after daphnetin intervention. This shows that NLR and SII do play a certain role in the occurrence and development of mastitis, which is consistent with the results reported by Wu Fengxueetal.[10], and daphnetin is of great significance in the treatment of mastitis. By comparing the levels of RDW-CV, NLR, PLR and SII in the blood of mastitis mice in group A, B and C, it was found that NLR and SII were significantly increased after mastitis infection (P<0.01), suggesting that NLR and SII can be used as diagnostic indicators of mastitis.
Normally, RDW-CV and PLR should also be related to the occurrence and development of mastitis, but there was no significant difference between them in this experiment (P>0.05), which may be due to the small number of subjects selected in the experiment. The levels of NLR and SII in the blood of mastitis mice after daphnetin intervention were significantly decreased (P<0.01), indicating that daphnetin plays an important role in the treatment ofS.aureus-induced mastitis.
In summary, NLR and SII showed high levels in mastitis mice, which had certain value in the auxiliary diagnosis of mastitis. After daphnetin intervention, both of them decreased significantly, indicating that daphnetin has a significant effect onS.aureus-induced mastitis is effective in mice and may contribute to the treatment of mastitis to some extent. However, there are still some shortcomings in this study: for example, the number of mastitis mice modeling groups is small, which may cause that the changes in RDW-CV and PLR levels have no obvious relationship with the occurrence and development of mastitis, thus affecting the experimental results, and more samples can be added for further study in the future.
- Medicinal Plant的其它文章
- Progress in the Application of Network Pharmacology in Mongolian Medicine Research
- Anti-tumor Effect of Paclitaxel Enhanced by Psoralen at the Cellular Level
- Preparation Process of Plumbagin Nanomicelle In-situ Gel
- Current Status and Prospects of Drugs for Ischemic Stroke Treatment
- Activity Screening Study on the Anti-tumor Effects of Extracts from Mahoniae caulis
- Effects of JAG-1 on the Proliferation and Migration of Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells after TRAIP Knockout

